Philippine
Languages
There are about 70 to 75
languages on the Philippine Islands. They belong to the
Indonesian branch of the Austronesian family and are
subdivided into two main subgroups - the central (or
Mesophilippine) division and the northern (or Cordilleran)
division - with a number of other member languages
forming smaller groups or remaining unclassified.
The most important languages in the central division are
Tagalog (a standardized form of which, Pilipino, is the
official national language) and Cebuano. The most
important in the northern division is Ilocano.
|
| Official
Name |
Repibilka ng
Pilipinas - Pilipino
Republic of the Philippines - English |
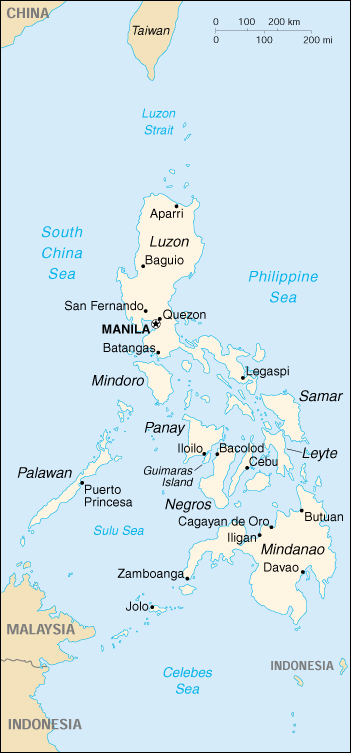
| Capital |
Manila |
| Official Languages |
Pilipino
English |
| Monetary Unit |
1 Philippine Peso ( P
) =
100 centavos |
Area
Size
|
| Regions |
sq mi |
sq km |
Bicol
|
6,808
|
17,633
|
Cagayan
Valley
|
10,362
|
26,838
|
Caraga
|
7,277 |
18,847 |
Central
Luzon
|
7,039 |
18,231 |
Central
Mindanao
|
5,549 |
14,373 |
| Central Visayas |
5,773
|
14,951
|
| Eastern Visayas |
8,275
|
21,432
|
| Ilocos |
4,958
|
12,840
|
| National Capital |
246
|
636
|
| Northern Mindanao |
5,418
|
14,033
|
| Southern Mindanao |
10,479
|
27,141
|
| Southern Tagalog |
18,117
|
46,924
|
| Western Mindanao |
6,194
|
16,042
|
| Western Visayas |
7,808
|
20,223
|
| Autonomous Regions |
| Cordillera |
7,063
|
18,294
|
| Muslim Mindanao |
4,493
|
11,638
|
Total
|
115,860
|
300,076
|
|