|
Assignment 3
| |
Introduction to Queries
Various Types of Queries
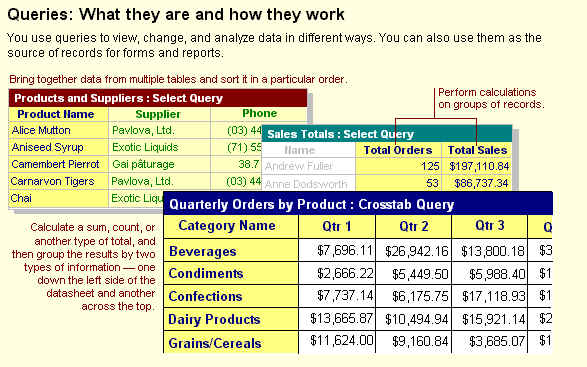
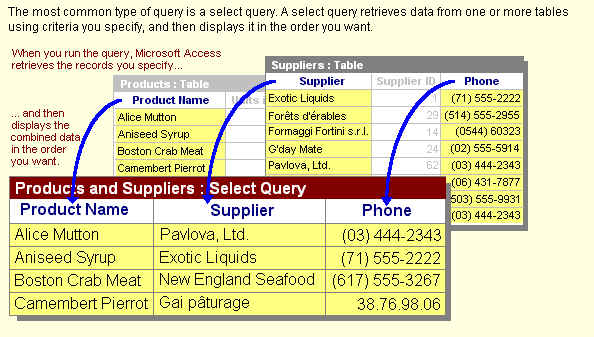
Select Query
A select query is the most common type of query. It retrieves data from one or more
tables and displays the results in a datasheet where you can update the records (with some
restrictions). You can also use a select query to group records and calculate sums,
counts, averages, and other types of totals.
Parameter Query
A parameter query is a query that when run displays its own dialog box prompting you
for information, such as criteria for retrieving records or a value you want to insert in
a field. You can design the query to prompt you for more than one piece of information;
for example, you can design it to prompt you for two dates. Microsoft Access can then
retrieve all records that fall between those two dates.
Parameter queries are also handy when used as the basis for forms and reports. For
example, you can create a monthly earnings report based on a parameter query. When you
print the report, Microsoft Access displays a dialog box asking for the month that you
want the report to cover. You enter a month and Microsoft Access prints the appropriate
report.
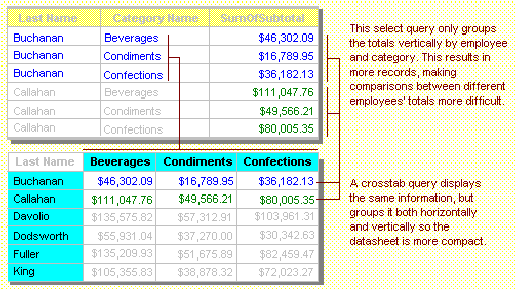
Crosstab Query
A crosstab query displays summarized values (sums, counts, and averages) from one field
in a table and groups them by one set of facts listed down the left side of the datasheet
and another set of facts listed across the top of the datasheet.
Example of a crosstab query
Crosstab queries calculate a sum, average, count, or other type of total for data that
is grouped by two types of information — one down the left side of the datasheet and
another across the top.
Action Query
An action query is a query that makes changes to many records in just one operation.
There are four types of action queries: delete, update, append, and make-table.
Delete Query
Deletes a group of records from one or more tables. For example, you could use a delete
query to remove products that are discontinued or for which there are no orders. With
delete queries, you always delete entire records, not just selected fields within records.
Update Query
Makes global changes to a group of records in one or more tables. For example, you can
raise prices by 10 percent for all dairy products, or you can raise salaries by 5 percent
for the people within a certain job category. With an update query, you can change data in
existing tables.
Append Query
Adds a group of records from one or more tables to the end of one or more tables. For
example, suppose that you acquire some new customers and a database containing a table of
information on those customers. To avoid typing all this information in, you'd like to
append it to your Customers table.
Make-table Query
Creates a new table from all or part of the data in one or more tables.
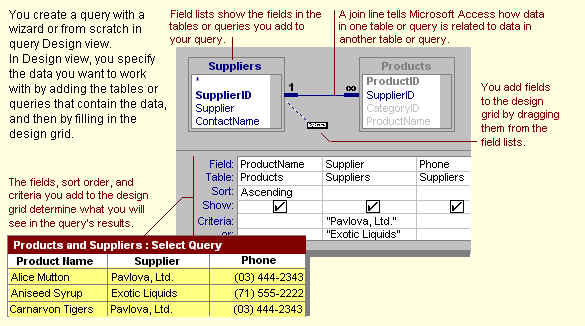
Method to Create a Select Query
- In the Database window, click the Queries tab, and then click New.
- In the New Query dialog box, click Design View, and then click OK.
- In the Show Table dialog box, click the tab that lists the objects whose data you want
to work with.
- Double-click the name of each object you want to add to the query, and then click Close.
- If you have multiple tables or queries in the query, make sure they are connected to
each other with a join line so that Microsoft Access knows how the information is related.
If they aren't connected, create the join line yourself.
- Add fields to the query by dragging the field names from the field list to the design
grid.
- Refine your query by entering criteria, adding a sort order, creating calculated fields,
computing the sum, average, count, or another type of total on the data it retrieves, or
otherwise modifying the query's design.
- To sort data, always put the Primary Sort Key in the first
column, the Second Sort Key in the second column and so on. In the sort row of the Query
Design view, indicate whether you want Ascending(A-Z) or Descending(Z-A) order.
- To save the query, click Save
 on
the toolbar. Enter a name that follows Microsoft Access object-naming rules, and then
click OK. on
the toolbar. Enter a name that follows Microsoft Access object-naming rules, and then
click OK.
- To see the results of the query, click View
 on the toolbar. on the toolbar.
Method to Create a Parameter Query
Create a parameter query that prompts for criteria each time it's run
A parameter query displays one or more predefined dialog boxes that prompt you for the
parameter value (criteria).
- Create a select or crosstab query.
- In query Design view, drag the fields from the field list to the query design grid.
- In the Criteria cell for each field you want to use as a parameter, type a prompt
enclosed in square brackets. Microsoft Access will display this prompt when the query is
run. The text of the prompt must be different from the field name, although it can include
the field name.
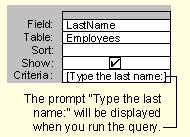
For a field that displays dates, you can display the prompts "Type the beginning
date:" and "Type the ending date:" to specify a range of values. In the
field's Criteria cell, type Between [Type the beginning date:] And [Type the ending
date:].
- To view the results, click the View button on the toolbar, and then type a value for the
parameter. To return to query Design view, click the View button on the toolbar again.
|