GENERAL
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Pilatus PC-7 Turbo Trainer is a low-wing monoplane with a tandem seating cockpit, powered by a Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-25A turboprop engine. The aircraft is designed for all aspects of basic through advanced flying training, including aerobatic, tactical and instrument flying. The Pilatus PC-7 Turbo Trainer has excellent flight characteristics and can be flown equally well from either cockpit. Solo flights are made from the front cockpit.
AIRCRAFT DATA
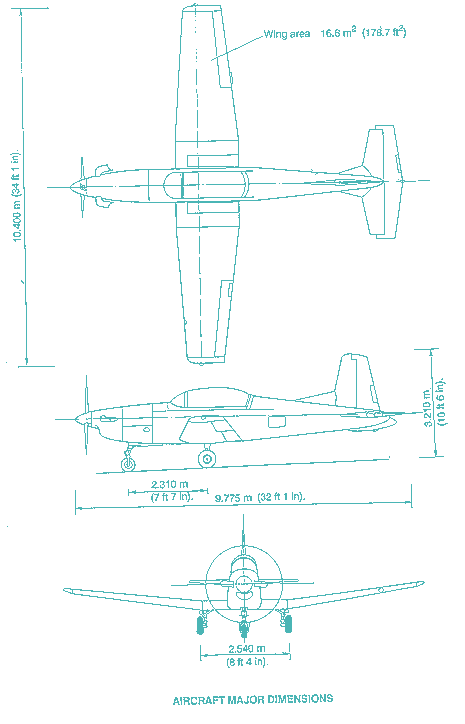
MAJOR DIMENSIONS
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WEIGHTS
Basic Empty Weight is defined as the complete aircraft, empty of usable fuel and without aircrew, baggage or underwing stores, but including engine oil and usable fuel. The basic empty weight depends on avionics fit but is approximately 1,350 kg (2,976 lb).
SPEEDS
EAS at max operating weight:
-
VMO 270 kts
- VFE,VLE
135 kts
- Stall with Idle power VS 71 kts VSO 64 kts
AIRFRAME SYSTEMS
STRUCTURES
Primary aircraft structure is of aluminium alloy in sheet or extruded form. Structural components share the structural loads.
The wing is a single-piece cantilever structure formed by a main spar, an auxiliary spar, ribs and stringer-reinforced skin. 6 hard points are integrated into the wing structure.
The fuselage is of semi-monocoque design formed by longerons, stringers, frames, a stainless steel fireproof bulkhead and skin.
LANDING GEAR (LG)
The LG is an electrically operated, retractable, tricycle-type system, controlled by mechanically interconnected controls from either cockpit. In the event of electrical system failure, the LG can be extended manually from the front cockpit.
Each LG leg is a conventional oleo-pneumatic shock absorber strut fitted with a single wheel. Each mainwheel is equipped with a direct operating, hydraulically actuated brake unit. The nosewheel shock absorber column swivels in its housing. It is retained in the neutral position by a spring-loaded cam and steering is achieved by differential braking.
Indication of LG position:
|
: three green lights illuminate in each LG control panel. |
|
: a red light illuminates in each LG control handle. |
|
: all LG position indication lights out |
A mechanical LG position indicator is located in the front cockpit.
FLIGHT CONTROLS
The primary control surfaces are manually operated from the front and rear cockpits by a conventional column and pedal system. Primary control surfaces are mass balanced.
Trim facilities are electrically actuated.
Flight controls can be locked from the front cockpit, with ailerons and rudder neutral, and elevator in the down position.
The split-type wing flaps are operated by an electrical acuator controlled by mechanically interconnected switches in both cockpits.
AIRCRAFT FUEL SYSTEM
Fuel is contained in two integral fuel tanks, with a total useable capacity of 474 litres (125.2 US gal). An aerobatic tank with a capacity of 12 litres (3.2 US gal) prevents engine fuel starvation during aerobatics and provides sufficient fuel for the permitted period of inverted flight. The aircraft fuel system delivers fuel to the engine fuel system at a rate and pressure in excess of the maximum engine requirement.
AIR CONDITIONING
Cockpit cooling is accomplished through a Freon-type cooling system consisting of an engine-driven compressor, a condenser and an evaporator, with a blower in each cockpit. The cockpit is heated and the windshield defogged (when required) by hot air bled from the engine compressor outlet. Controls in the front cockpit allow ram air and/or hot bleed air to be selected to the floor outlets of both cockpits and/or the windshield of the front cockpit.
OXYGEN
The gaseous oxygen system is of the economical diluter/demand type and provides both pilots with either oxygen diluted with cockpit air in proportions varying automatically with altitude or, when necessary, with pure (100%) oxygen.
ELECTRICAL POWER
Electrical power for the various user systems consists of a primary 28 VDC system, a secondary 24 VDC system and two AC output static inverters. Primary 28 VDC power is supplied by the dual-role starter/generator. A 24 V / 40 Ah nickel/cadmium battery forms the secondary DC power source.
With the aircraft on the ground and the engine shut down, DC power is obtained from the battery or an external power.
AC power (for navigation and avionic equipment) is supplied by one of the two identical static inverters, the remaining inverter is used as a standby. Each inverter provides two outputs: 115 VAC, 400 Hz and 26 VAC, 400 Hz.
LIGHTING
The navigation lights comprise a red light on the LH wing tip, a green light on the RH wing tip and a white light on the tail. An anti-collision strobe light is combined with each colored navigation light. A 250 watt landing/taxi light is mounted on each main landing gear strut. Instruments and panels are equipped with internal blue/white lighting.
ICE PROTECTION
Ice protection consists of:
-
an engine intake air inertial separation system which complies with the requirement of FAR 25.
- an
electrical heating system for the pitot tube, static ports, fuel
sense line and angle-of-attack (AOA) transmitter.
- a propeller de-icing system (optional).
Flight into known or forecast icing conditions is not approved.
PROPULSION SYSTEMS
ENGINE
The engine is a Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-25A, free turbine, turboprop engine with full aerobatic capability.
Configuration
-
Three axial plus one centrifugal stage compressor,
- Annular
combustion chamber,
- Single
stage compressor turbine,
- Single stage power turbine.
PROPELLER
The Hartzell HC-B3TN-2 constant speed and feathering propeller is controlled by a propeller governor/constant-speed unit (CSU) at between 1,825 and 2,200 rpm according to the position of an RPM lever located in each cockpit. Protection against propeller overspeed is provided by an overspeed governor and a free turbine speed (Nf) governor within the CSU.
AVIONICS
COMMS
In accordance with customer requirements.
NAV
In accordance with customer requirements.
INSTRUMENTATION
Each cockpit is equipped with the following standard instrumentation:
-
Airspeed indicator (in knots).
- Attitude indicator.
- Turn and
bank indicator.
- Altimeter
(in feet, barometric indication in millibars).
- Vertical
speed indicator (in feet per minute).
- Angle of
attack indexer.
- Clock.
- Accelerometer.
- Magnetic compass.
- Aileron,
rudder and elevator trim position indicators.
- Engine
torque pressure indicator (in psi).
- Engine
interturbine temperature (ITT) indicator (in 0C).
- Engine gas
generator speed (Ng) indicator (in % rpm).
- Engine oil
temperature/pressure indicator (in 0C/psi).
- Propeller
speed (Np) indicator (in rpm).
- Fuel flow
indicator (in lb/hr).
- Fuel quantity indicator (in fractions of total capacity).
In addition, the front cockpit is equipped with a fuel totalizer and an engine air inlet temperature indicator.