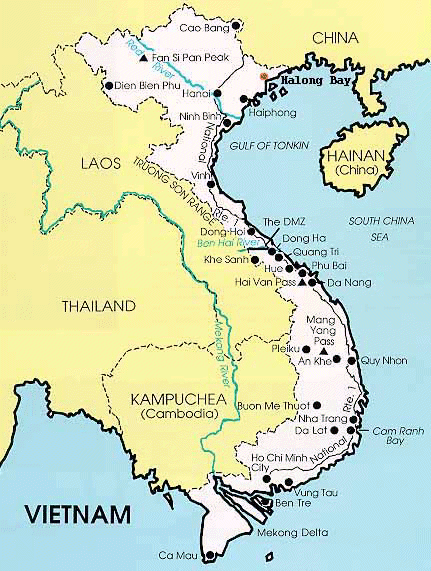
Vietnam is easily identified as a long strip of land that resemble an "s". Aside from delta region and coastal plain,Vietnam is covered by Hills and mountain. The people depends on the land to live each day.
Vietnam is divided into three geographical region. Bac is the north , Nam is the south and Trung which is the last region.

Trung, Middle region
Extending from North to South,the Truong Son Mountain is six thousand five hundred feet above sea level and separate Vietnam form Laos and Cambodia. Near the South of the Troung Son Mountains lives minorities of Vietnam. These groung are known as the Ra De and Jarai. To foreigners they are commonly known as the mountain people. Mountain people enjoys the pleasant climate and the relaxed atmosphere away from the city. Government have urged and have set bills to enticed more Vietnamese to move toward the mountain. The North and South have become increasingly overcrowded.
Bac, The North
Rice field and rugged mountain of the red river Delta makes up the landscape of Bac. Water are abundant and rice field are grown throughout the land. Rice provide food for the twenty million populated rural area. However the North has problem with flooding. Mostly between the months of June and October, water may rise up to thirty three feet in a day.
Nam, The South
Lies between the Mekong Delta the lands of Nam are very rich and fertile. "Unlike the Red River Delta, the Mekong delta is filled with numerous minor tributaries and outlet that branch from the Mekong's nine great tribritaries (Cavendish,13). It is also Asia's longest river. It stretches from Tangu through Tibet, into Laos then through Thailand, runs through Cambodia and into Vietnam. Although the land is not rich for rice like the north the people compensate. The grow and imports. Unlike the North Flooding is not a major problem.

