INERTIA: The tendency
of all objects and matter in the universe to stay still if still,
or if moving to go on moving in the same direction unless acted on by some outside force.
FORCE: A force is a
push or pull upon an object resulting the object's interaction with
another object. It is a vector quantity, and its unit is N(Newton) in S.I unit system.
APPLIED FORCE: An
applied force is a force which is applied to an object by a person or
another object. If a person is pushing a desk across the room, then there is an applied
force acting upon the object. The applied force is the force exerted on the desk by the
person.
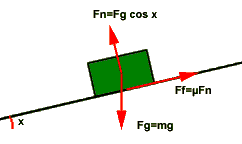
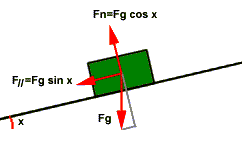
GRAVITATIONAL FORCE (Fg):
The force of gravity is the force at which the earth, moon, or
other massively large object attracts another object towards itself. By definition, this
is the weight of the object. All objects upon earth experience a force of gravity which is
directed downward towards the centre of the earth. The force of gravity on earth is always
equal to the weight of the object as found by the equation:
Fg = m x g where g=m/s2 (on Earth)
and m=mass (in kg)
NORMAL FORCE (FN): The normal force is the support force exerted upon
an object which is in
contact with another stable object. For example, if a book is resting upon a surface, the
surface is exerting an upward force upon the book in order to support the weight of the
book. On occasions, a normal force is exerted horizontally between two objects which are
in contact with each other.

FRICTIONAL FORCE (Ff): The frictional force is the force exerted by a
surface as an object
moves across it. The frictional force opposes the motion of the object. For example, if
a book moves across the surface of a desk, then the desk exerts a frictional force in the
opposite direction of its motion. The frictional force can be calculated using the
equation:
Ff = � x FN � = coefficient of friction