

By Kepler Ryan and Dylan Roberts.
KEY WORDS.
Alkaline, earth, metals, chemicals, elements, science, chemistry, properties, beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium, radium, alkaline earth metals, chemical, physical and pyrotechnics.
INTRODUCTION.
Alkaline Earth Metals occupy the second column of the periodic table of elements. They consist of beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, barium and radium. Magnesium and calcium are the most abundant alkaline earth metals in the earths crust; they are also the most important of the family for commerce. 4
CHARACTERISTICS of ALKALINE EARTH METALS.
General Alkaline Earth Metals.
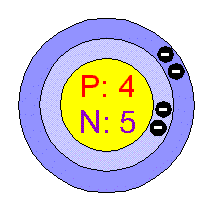
BERYLLIUM.
General Data.
Beryllium is fourth on the periodic table (after H, He and Li). It was discovered in 1798 and first isolated from other elements in 1828 independently by Friedrich WÖhler and Antoine Bussy. It was not widely used in industry until the 1940s and 50s. 7
Today Beryllium is used for:
The speed of sound in
Beryllium is 12,500 metres per second and is greater than in any other element.
Physical Properties.
Beryllium is the lightest
of the rigid metals and is also one of the lightest of all elements.
It is extremely strong and hard being six times stiffer than steel.
It is rather elastic and has a high melting point of 1,287 degrees Celsius and
a boiling point of 2500 degrees.
It is a greyish metal, but in compounds beryllium can be a blue-green colour
called aquamarine.
Beryllium is non magnetic and has a high permeability to x-rays.
It has a hexagonal crystal structure and has a density of 1.8477 grams per centimetre
cubed. 4
Chemical Properties.
Beryllium
has high resistance to both heat and corrosion, has a high heat absorption capacity
and can be produced to very close tolerances.
Aquamarine and emerald are precious forms of the compound beryl, [Be3Al2(SiO3)6]
Pure Beryllium maybe obtained by electrolysis of molten BeCl2 containing some
NaCl.
The salt is added since the molten BeCl2 conducts very poorly.
Another method involves the reduction of beryllium fluoride with magnesium at
1300 degrees Celsius. 8
BeF2 + Mg ---> MgF2 + Be
 4
4
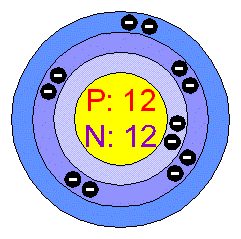
MAGNESIUM.
General Data.
Magnesium has an atomic
number of twelve and is the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust.
It was discovered and isolated in 1808 by Sir Humphrey Davy, a British chemist.
He produced the metal by electrolyzing a mixture of moist magnesia and mercuric
oxide, then evaporating the magnesium from the mixture.
It is obtained today mainly by electrolysis of fused magnesium chloride.
Magnesium is used for:
Physical Properties.
Magnesium is the lightest
common metal, as it weighs one third less than aluminum.
Its melting point is 650 degrees Celsius and magnesium's boiling point is 1107
degrees Celsius.
It has a hexagonal crystal structure, a density of 1.738 grams per centimeters
cubed and is grey in colour.
Magnesium is malleable and ductile when heated. 9
Chemical Properties.
The metal is not attacked
by oxygen, water or alkaline at room temperature; it reacts with acids.
When heated to approximately 800 degrees Celsius it reacts with oxygen and emits
a brilliant white light.
Look above in the section on 'uses' for more chemical properties. 7
CLICK HERE TO VIEW A QUICKTIME MOVIE OF MAGNESIUM BURNING! (0.5mb)9

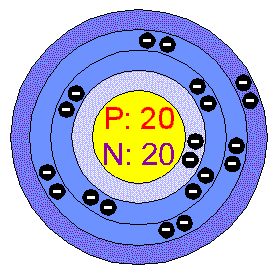
CALCIUM.
General Data.
Calcium is the fifth
most abundant element in the earths crust.
Its atomic number is 20.
Like magnesium the British chemist Sir Humphrey Davy also isolated calcium in
1808 by means of Electrolysis.
Calcium does not occur freely in nature but is found in many chemical compounds
such as limestone, marble, chalk, Iceland spar, coral, pearls and eggshells
that are all made of the compound calcium carbonate.
The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of fused calcium chloride, which
deems very costly.
Calcium is a very important element for our bodies as it aids in the construction
of bones and teeth and is the most common metallic element in our bodies. 8
Physical Properties.
Calcium is a malleable
and ductile metal; Calcium rapidly tarnishes to yellow on contact with air (This
is a good indication that your compound is Calcium).
The melting point of Calcium is 839 degrees Celsius and it boils at 1484 degrees
Celsius.
It has a silvery colour and is moderately hard. 5
Chemical Properties.
When calcium
burns it forms a yellow-red flame, it will eagerly form a white coating of nitride
in air, and will react with water.
It is used as a reducing agent and is also a deoxidizer, a desulfurizer and
a decarburizer.
The most important compound of Calcium is quicklime (CaO), which is a major
component in cement. Calcium
can be made through the reduction of CaO with aluminum or of CaCl2 with sodium
metal.
6CaO + 2Al ---> 3Ca + Ca3Al2O6 CaCl2 + 2Na ---> Ca + 2NaCl
 10
10
STRONTIUM.
General Data.
Strontium was detected
by William Cruikshank in 1787, but it was not first isolated until 1808 by Sir
Humphrey Davy.
Strontium is one of the best sources for nuclear power, space vehicles, weather
stations and navigational buoys.
Strontium Nitrate is utilized in flares and pyrotechnic devices because it burns
with an intense red flame.
Strontium sulfide has luminescent properties and is used in certain types of
luminous paint.
It does not occur as a free element. 5
Physical Properties.
Strontium is softer than
Calcium and decomposes water with vigor.
Fresh Strontium has a silvery appearance, but rapidly turns to a yellowish colour
with formation of the oxide.
Strontium salts give an excellent crimson colour to flames, and are used in
pyrotechnics.
Strontium's melting point is approximately 769 degrees Celsius and it will boil
at 1384 degrees Celsius. 6
Chemical Properties.
Strontium will ignite
suddenly in air when divided finely.
Strontium is
made commercially on small scale by the electrolysis of molten strontium chloride.
SrCl2. Sr2+(l) + 2e- ---> Sr Cl-(l) 1/2Cl2 (g) + e-
Strontium metal can also be isolated from the reduction of strontium oxide, SrO, with aluminum. 8
6SrO + 2Al ---> 3Sr + Sr3Al2O6


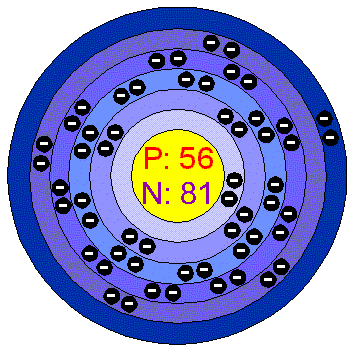
BARIUM.
General Data.
The atomic number of
Barium is 56.
Barium has few practical applications, it is some times used for coating conductors
in electrical components; Barium Sulfate (BaSO4) is used as a filter for rubber
products, in paint and in linoleum.
Barium Nitrate is used in fireworks and Barium Carbonate is used in rat poisons.
Barium was first isolated and discovered in 1808 by Sir Humphrey Davies. 11
Physical Properties.
Barium's Crystal structure
is cubic.
Barium is soft, silvery and highly reactive.
This element melts at 725 degrees Celsius and it will boil at approximately
1640 degrees Celsius.
Barium is highly insoluble.
Chemical Properties.
Barium is made on small scale by the electrolysis of molten barium chloride.
BaCl2. Ba2+(l) + 2e- Ba ---> Cl-(l) 1/2Cl2 (g) + e-
Barium metal can also be isolated from the reduction of barium oxide, BaO, with aluminum.
6BaO + 2Al ---> 3Ba + Ba3Al2O6 11
 11
11
RADIUM.
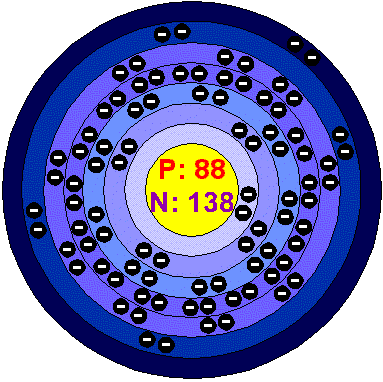
General Data.
The atomic number of
Radium is 88.
Radium was discovered in the ore pitchblende by the French chemists Marie Curie
and Pierre Curie in 1898.
Radium is extracted from Uranium ore with approximately one part of Radium per
3 million of Uranium.
Radiation from Radium has a harmful effect on human cells, and Radium burns
are caused by overexposure to the rays.
Radium is used in the treatment of only a few kinds of cancer; radium chloride
or radium bromide is inserted into the diseased tissue.
Small amounts of Radium were once used in the production of luminous paint,
which was applied to clock dials, doorknobs, and other objects to make them
glow in the dark. 5
Physical Properties.
The melting point of
Radium is 700 degrees Celsius.
Its crystal structure is cubic.
It is brilliant white, luminescent, highly radioactive metallic element.
Radium has a density of 5 grams per milliliter.
The oxide of Radium has a strong base. 12
Chemical Properties.
Radium will oxidize on
exposure to air.
Radium is handled in the form of Radium Bromide and Radium Chloride and practically
never in the metallic state.
The chemical properties of Barium are similar to those of Barium.
Radium likes to combine with acids.
The metal can be obtained by distillation using the following formula:
Ra2+(l) + 2e- ---> Ra Cl-(l) ---> 1/2Cl2(g) + e-
 2
2
FOOTNOTES.