HONG KONG ADVANCED LEVEL EXAMINATION
AL PHYSICS
1993 Essay Type Question
1. (a) State the differences between a steady flow and a turbulent flow of fluids.
(3 marks)
(b) In the steady flow of a liquid through a narrow pipe, explain how a velocity gradient is set up. (3 marks)
(c) A block of base area A lies on a horizontal lubricated floor. The lubricant is a layer of liquid having thickness t and coefficient of viscosity h . Derive the force required to move the block at a constant velocity v. Briefly explain each step in your argument and state the assumption(s) you made. (4 marks)
(d) The viscosity of a liquid can be measured by using Stokes’ law. Ball-bearings are dropped into a long vertical glass tube containing the liquid and their respective terminal velocities are measured for calculating the coefficient of viscosity of the liquid. State and explain the precautions in performing this experiment. (No mathematical derivation is expected.) (6 marks)
2. (a) Describe FOUR contrasting features of progressive and stationary waves, and state the conditions necessary for a stationary wave. (6 marks)
(b) Beats can be heard when a tuning fork and a guitar string vibrate simultaneously with slightly different frequencies f1 and f2 respectively.
(ii) Show that the beat frequency is equal to the difference between f1 and f2.
(7 marks)
(c) Briefly describe how the principle of beats would be used to detect the speed of cars in a police radar speed check system. (No mathematical derivation is expected.) (3 marks)
3. (a) State the order of magnitude of
(i) the average drift velocity of electrons in a current-carrying wire;
(ii) the speed of electrical signals in a circuit.
(b) Derive the current flow equation i = nAve fro a metal wire. Explain the meanings of the symbols in the equation. (3 marks)
(c) Draw a labelled diagram of a moving-coil meter. Briefly describe its working principles and explain how a linear scale may be achieved. (8 marks)
4. (a) Explain each of the three terms in Einstein𠏋 photoelectric equation 練vm2 = hn - f . (2 marks)
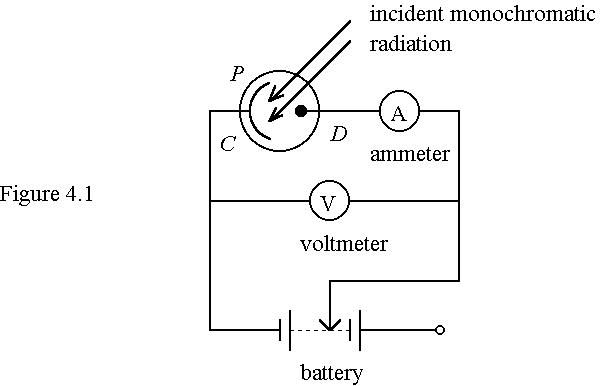
(b) Figure 4.1 illustrates the basic features of the laboratory apparatus for investigating photoelectricity. It contains a vacuum photoelectric cell P with a photosensitive metal C of large area and a collector of electrons D.

(ii) Copy the graph you have drawn in (i) and sketch on it the curves for
(I) increased light intensity, with the light frequency being kept constant;
(II) increased light frequency, with the light intensity being kept constant.
Explain briefly. (9 marks)
(c) Briefly describe the use of photoelectric cells in the reproduction of sound from film soundtracks. (2 marks)
(d) Photoelectric emission is one of the phenomena that demonstrate the particle-like properties of electromagnetic radiation. Briefly describe an experiment to show that particles such as electrons also exhibit wave-like properties.
(3 marks)
5. (a) (i) Briefly describe an experiment to investigate the r.m.s. current in an LRC series circuit for different frequencies of an a.c. supply. (No mathematical derivation is expected.)
(ii) Sketch a graph showing how the r.m.s. current in the circuit varies with the applied frequency. Account for the shape of the curve with the aid of phasor diagrams.
(iii) Sketch, on the same graph in (ii), the curves for
(I) smaller resistance;
(II) larger resistance.
(11 marks)
(b) Figure 5.1 shows a simplified tuning circuit for radio receivers.
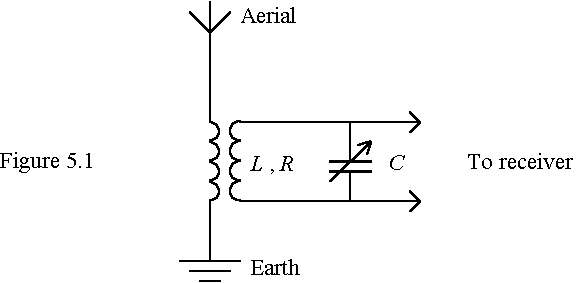
(i) Explain its operation.
(ii) Suggest a method to improve the reception performance of the circuit. Explain briefly.
(5 marks)
6. (a) An ideal spring of force constant k is mounted horizontally with one end fixed and the other end attached to a block of mass m (as shown). The block is set to oscillate with amplitude A on a level, frictionless surface.
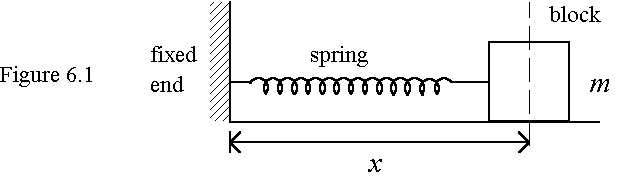
(i) Sketch a graph of elastic potential energy U against x for the spring-mass system, where x is the distance of the block from the fixed end. Mark on the graph the position xc of the central point of the oscillatory motion.
(ii) On the same graph in (i), use a dotted line to sketch the graph of kinetic energy of the system against x. Briefly explain your graph by using energy-based arguments.
(4 marks)
(b) In (a), the spring is assumed to have negligible mass. However, no spring is completely massless. To find the effect of the spring𠏋 mass, consider a spring of mass M and force constant k. When the spring is stretched or compressed by an amount e, the elastic potential energy is 糊e2.
(Hint: find the mass of the speed of each spring element of length dl.)
(ii) Find the extension of the spring in terms of x and write down the expression for the total energy of such an oscillating spring-mass system. Take the time derivative of the expression and find the period of the subsequent motion.
(10 marks)
(c) How does the motion change if the oscillating system is immersed in water?
(2 marks)
- End of Paper -