Amino acids
-over 170 a.a. are known to occur in cells and tissues. Of these, 26 are
constituents of proteins and 20 occur commonly in protein
-plants are able to make a.a., animals are unable to synthesis all they need. And they
must obtain some 'ready-made' amino acids from their diet. These are called essential
amino acids, those that can be synthesized by the organism itself are known as
non-essential amino acids.
Structure of amino acids
- most a.a. possesses one acidic carboxylic group and one basic amino group. And they are
called neutral amino acids. The general formula of amino acid is shown below.
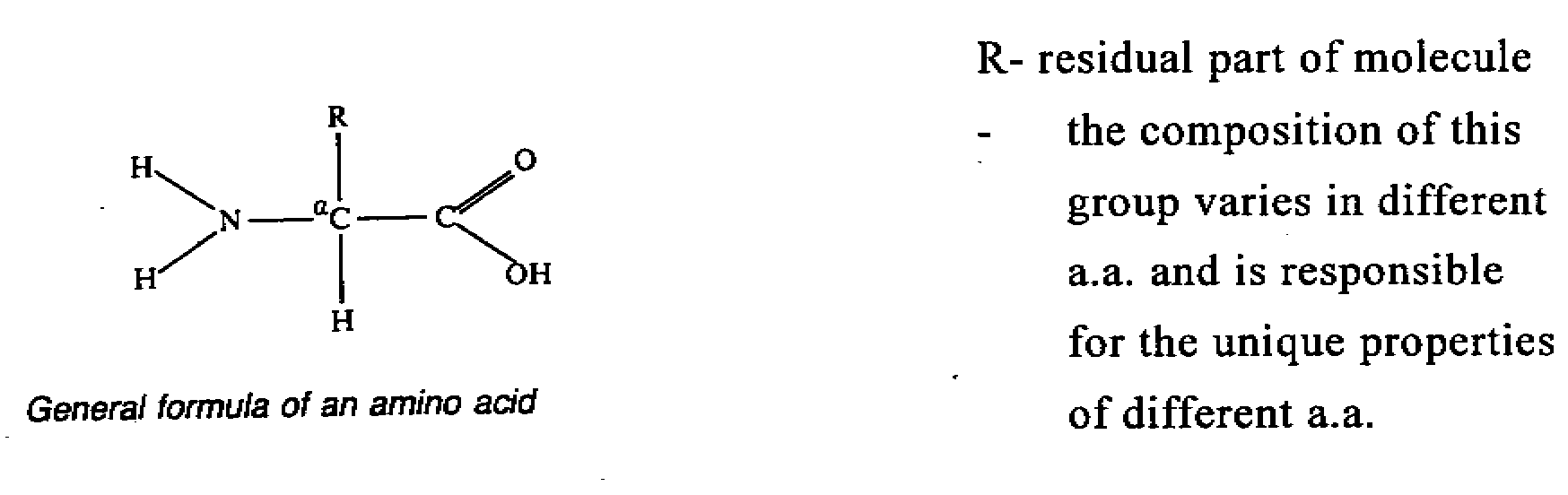
There may be more than
one amino group and they are called basic amino acids. For those which
possess more than one
carboxylic group are known as acidic amino acid.
The simplest a.a. is glycine where R is substituted by H. For other
a.a., R group is not H and so all the four group attached to the carbon atom are different
and so an asymmetric carbon is formed. This means that these a.a. all possess two
optically active forms. All a.a. except glycine possess D and L forms. In nature, a.a. are
generally found in L-form.

Properties of amino acids
- amino acids are colourless, crystalline solids
- they are soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents
- in neutral aqueous solution, a.a. exist as dipolar ions(Zwitterion) and are
amphoteric i.e.
poses both basic and acid properties.
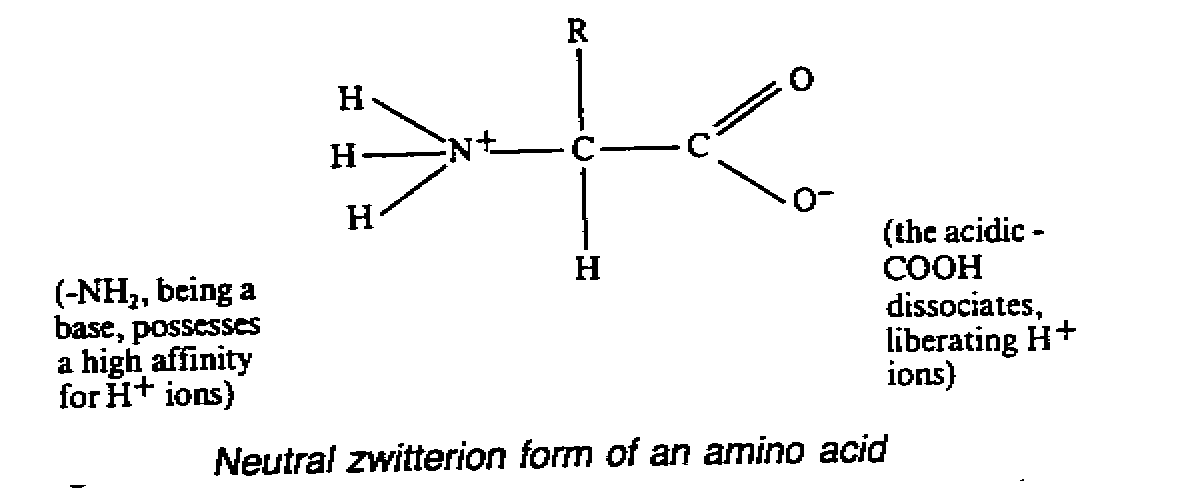
- each a.a. has its own specific pH at which it will exist in its neutral zwitterion.
If it is placed in an electric field at this pH, the a.a. will neither migrate to cathodes
or anodes and this pH is called its isoelectric point.
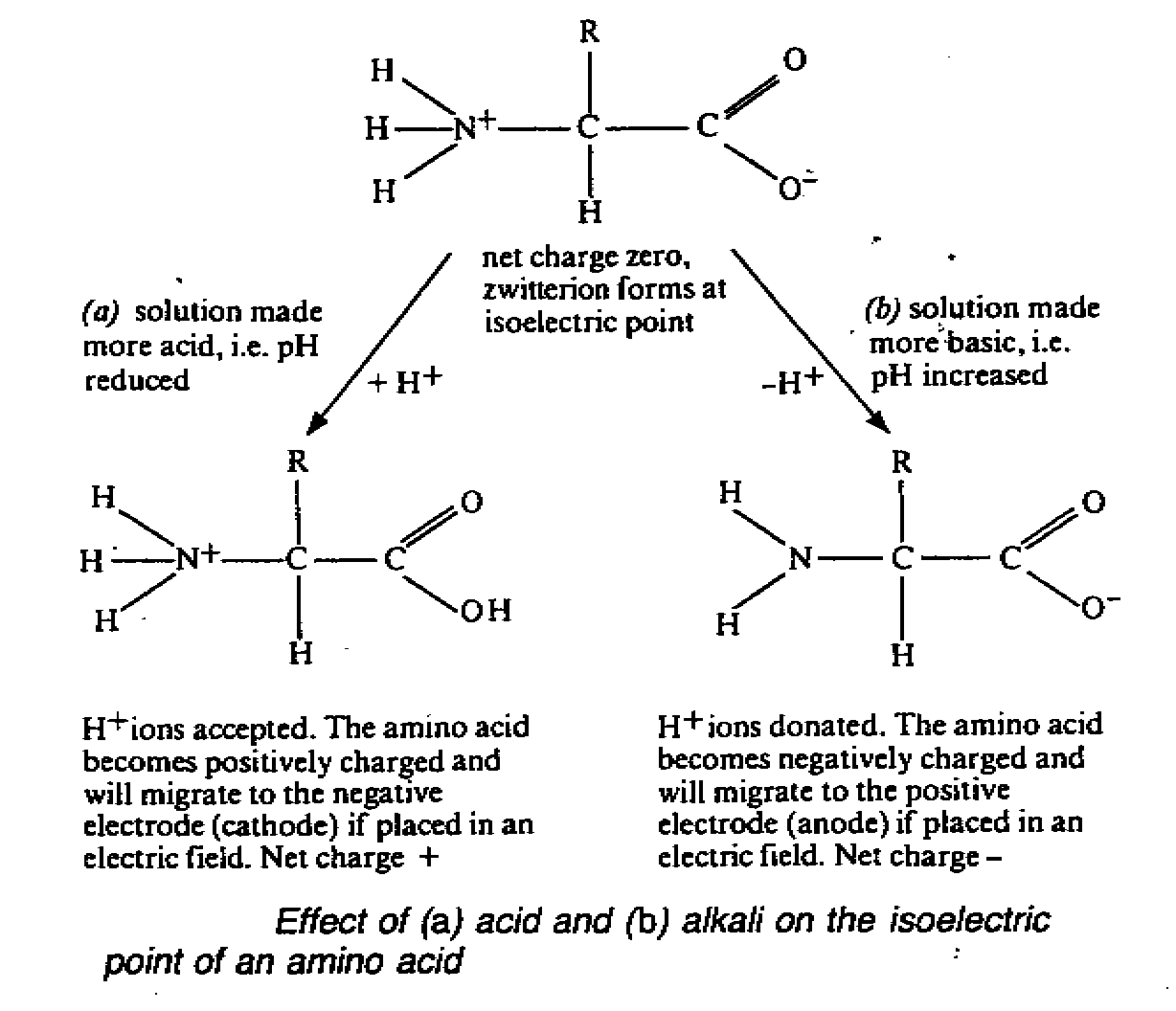
- the amphoteric nature of a.a. cause it to act as buffer in solutions,resisting
changes in pH The following diagram shows how an a.a. resist pH changes:
- a.a. can form variety linkage with other reactive groups
1. Peptide bonds
- amino group of one amino acid and carboxylic group of another a.a. can link together
by the elimination of one water molecule(condensation) . The covalent bond formed is
called peptide bond.
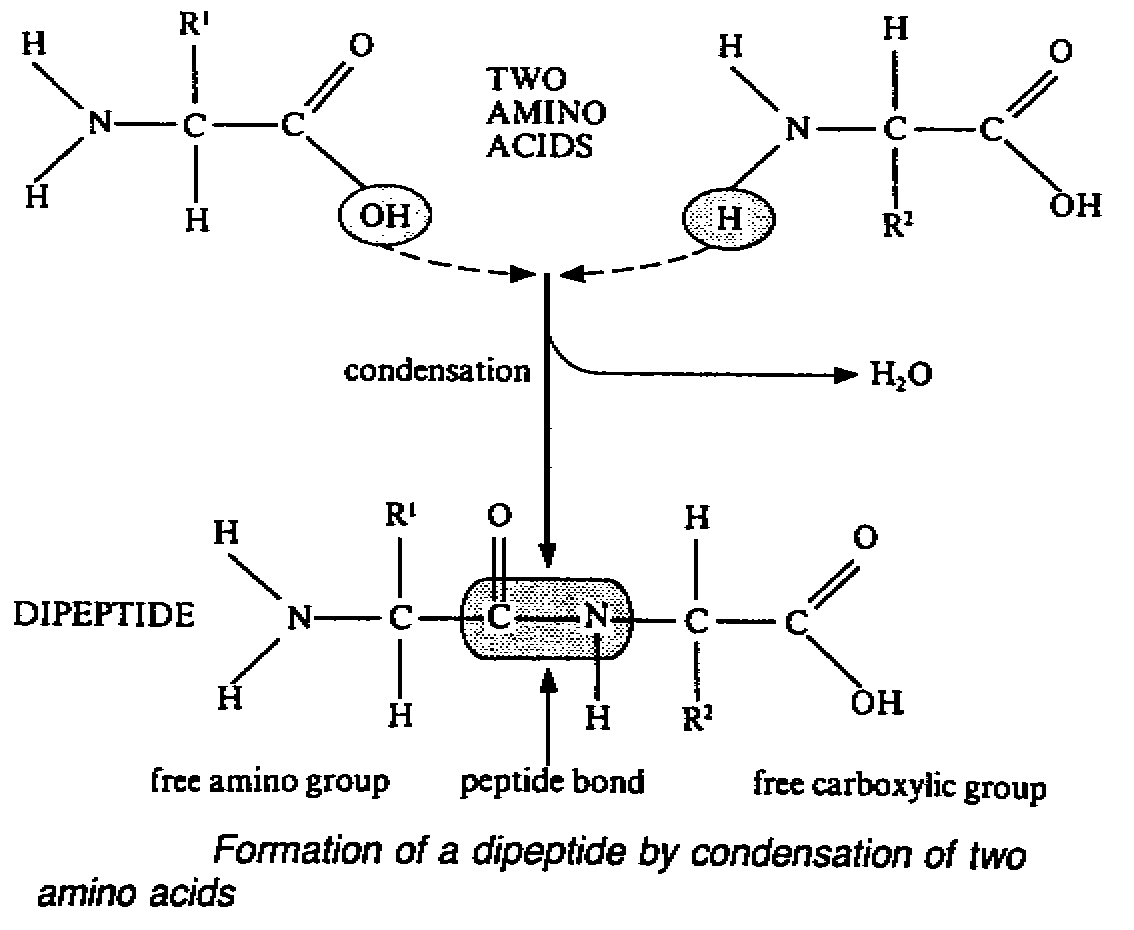
- a dipeptide possesses a free amino group at one end and a free carboxylic group at
the other. This enable further combination with other amino acids. If many a.a. are joined
in this way it is called a polypeptide.
2. ionic bond
- at suitable pH, an interaction may occur between ionized amino group and carboxylic
group. This results in formation of ionic bond.
3. Disulphide bond
- two sulphydryl(-SH) group of neighbouring amino acid may combine to form disulphide
bond.
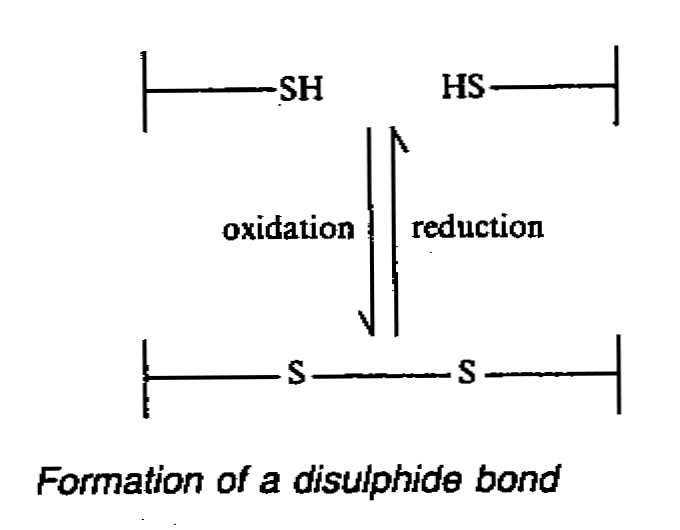
4. Hydrogen bond
- electropositive H atoms attached to 0 or N of -OH and -NH2 groups has a tendency to
share the e- of neighbouring electronegative oxygen atom such as O of a =CO
group. This sharing of electron formed the hydrogen bond which is quite weak. But as it
occurs at a high frequency, the total effect of them makes a considerable contribution
towards molecular stability.
Proteins
- they are complex organic compound containing C, H, 0 and N sometimes S
- they are polymer made up of amino acids
- twenty different amino acids are commonly found in naturally occurring proteins. The
potential variety of protein is
unlimited because the sequence of a.a. in each protein is specific. Number, types and
sequence of a.a. in polypeptide can vary infinitely due to different combination of 20
a.a. and this gives a large variety of proteins. Also 3-D folding and bonding of
polypeptide chains in different ways cause variety of proteins to be formed. Folding of
chains into globular protein enables protein to perform metabolic function e.g. enzyme.
Different arrangement of polypeptides into fibrous protein provide mechanical strength for
structural protein.
- they are the most abundant organic molecules found in cells
- each protein possesses a characteristic three-dimensional shape, it is usual to refer to
four separate levels of organisation as follows:
Primary structure
- it is the number and sequence of a.a. held together by peptide bonds in polypeptide.
- the sequence of a.a. dictates its biological function and this sequence is strictly
controlled by sequence of bases in DNA
Secondary structure
- it describe the folding of polypeptide chains
- it usually takes the form of an extended spiral spring, the α-
helix, whose structure is maintained by many hydrogen bonds formed between adjacent CO and
-NH2 group.(The H atom of the NH2 group of one,a.a. is bonded to the
O atom of the CO group three amino acids away)
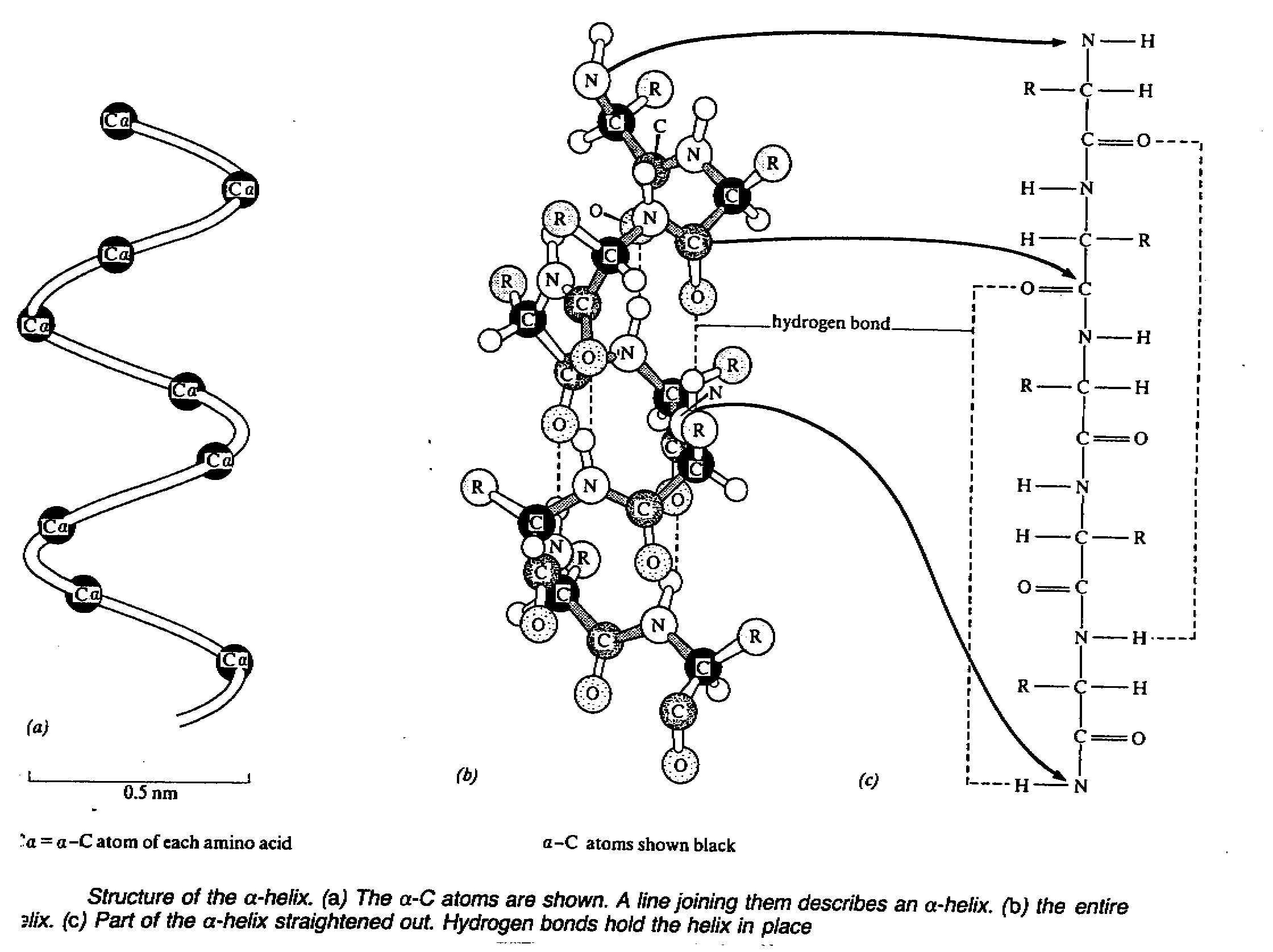
- theroretically, all CO and NH2 group can participate in hydrogen bond, so is
very stable and common structure
- another type of 2nd structure is the β-
pleated sheet
- this structure comprises a number of adjacent chains which are more extended than the α- helices. They are arranged in a parallel fashion but
runnign in opposite directions to one another. They are joined together by hydrogen bonds
formed between CO and NH2 group of one chain and NH2 and CO groups of adjacent
chain. This structure involve a lot o hydrogen bonds and so the structure is very stable.
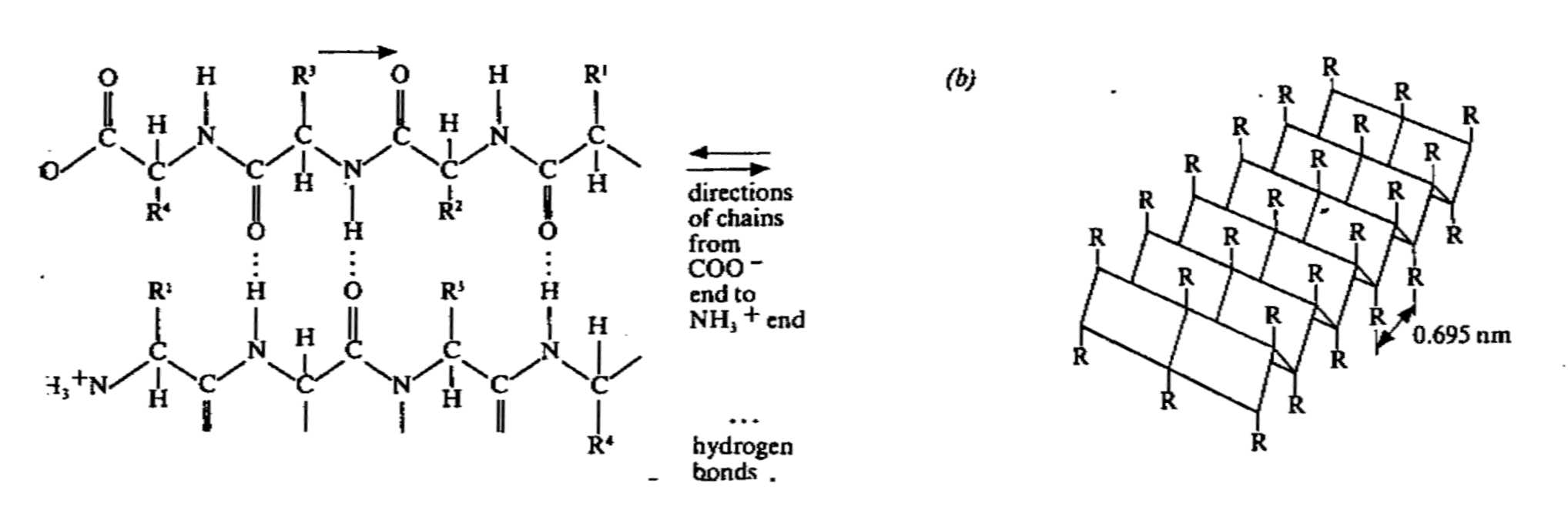
- The protein with structure of a β-pleated sheet has a
high tensile strength and cannot be stretched.
- Another arrangement of 2nd structure is that 3 polypeptide chains would
around each other to form a triple helix.
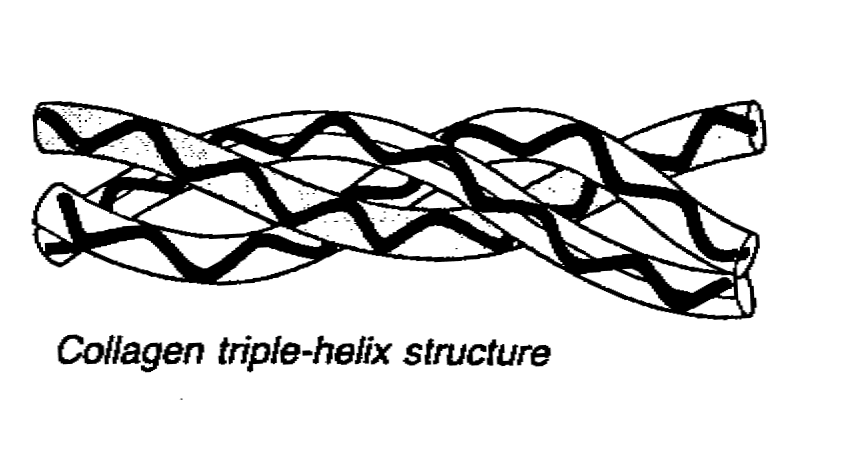
Tertiary structure
- it describes the way in which the helix fold to form compact structure
usually the polypeptide chain polypeptide chain bends and folds extensively, forming
a precise, compact globular shape. This is
the tertiary structure of protein
- it is maintained by interaction of the 3 types of bonds, namely ionic, hydrogen and
disulphide bridge as well as hydrophobic interaction
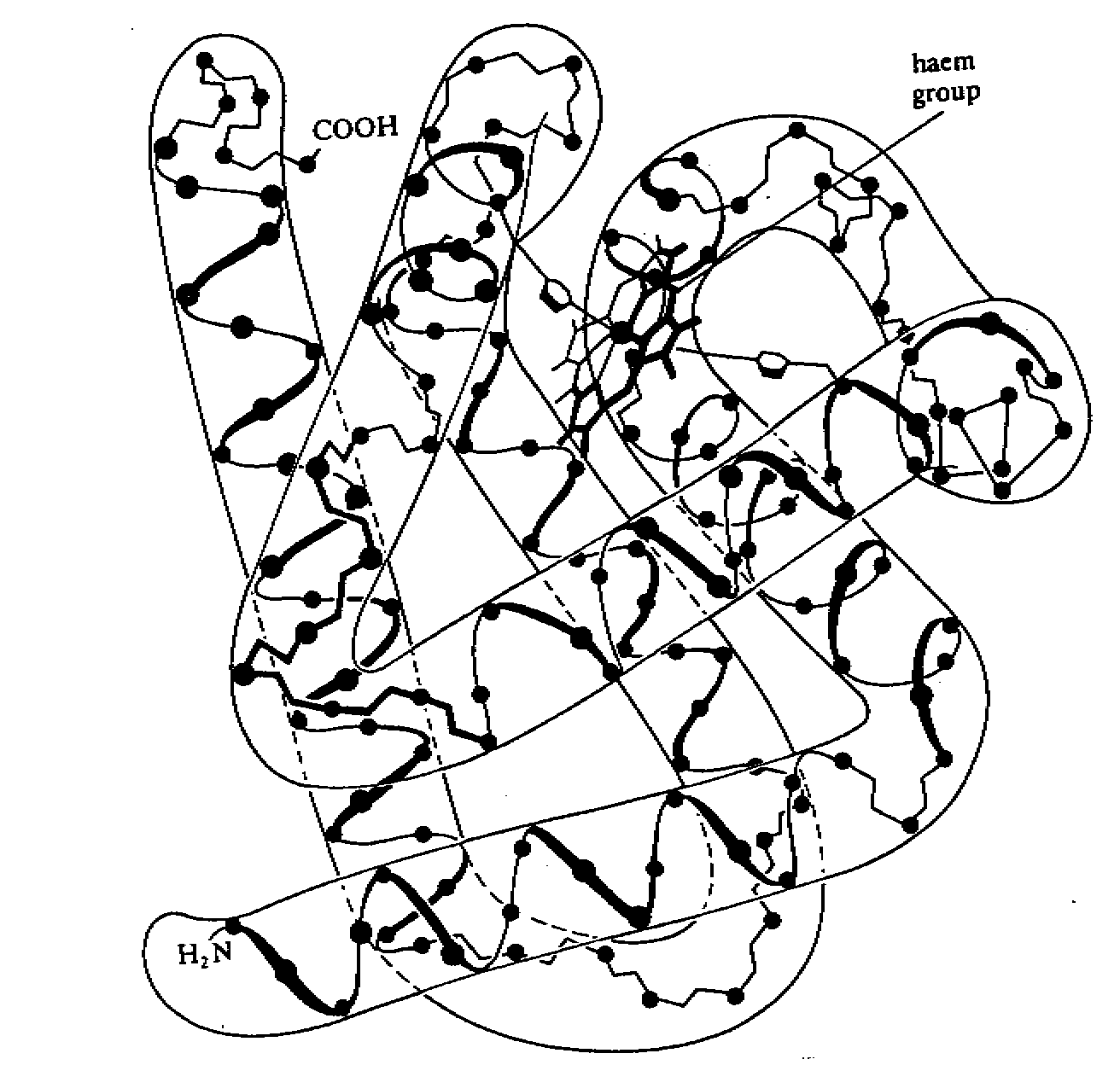
Quaternary structure
- it describes the structure where polypeptides may aggregate to form large structure
- many highly complex proteins consist of an aggregation of polypeptide chains held
together by hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen and ionic bonds. This precise arrangement is
the quaternary structure e.g. haemoglobin consists of 4 polypeptide chains held together









