
The international standard
ISO 9283 (Manipulating Industrial Robots - Performance Criteria and
Related Test Methods) which
has become the European standard EN 29283 has deficiencies
hindering broad industrial
use.
However, a broad industrial
acceptance and utilisation of this type of accuracy standard by robot
manufacturers and users
would enable true comparisons to be made between robots and thus, help
to
avoid bad economic decisions.
Therefore, the goals
of the project are:
- Inquiry-based investigation
of robot test procedures and test equipment applied at European robot
users.
- Determination and analysis
of robot-user's requirements for robot performance criteria, testing
procedures and related measurement
equipment.
- Classification of different
robot test procedures in function of robot applications, enabling the robot
user (particularly SMEs)
to select the right robot for his application. - Improvement of performance
criteria, and related measurement
and evaluation methods/procedures for industrial robots.
During the first 6
months project duration, questionnaires on robot testing were prepared
and sent to
approx. 4000 robot users,
manufacturers and research institutions. More than 100 responses
obtained so far, already
indicate some clear tendencies and needs for improvement of robot testing.
Finally, the project will provide the following achievements to European industry and SMEs:
- Further development and
validation of automated measurement systems for EN 29283 / ISO 9283
and criteria with better
reliability (including implementation of a software system for performance
criteria and testing methods).
- Dissemination of the standard
and determination system to European users and manufacturers of
industrial robots.
- Contribution to the revision
of ISO 9283 initiated by ISO TC184 / SC2 / WG2.
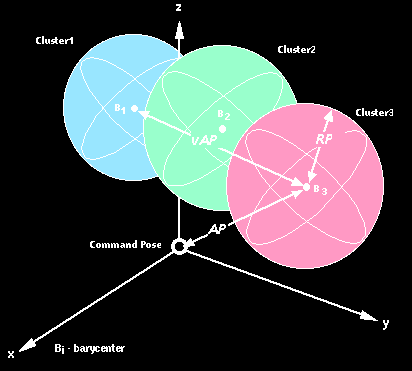
Multi-directional pose accuracy variation:
Multi-directional pose accuracy variation expresses
the deviation between the different mean attained poses
achieved when visiting the same command pose n times
from three orthogonal directions, see figure 1.
- vAP is the maximum
distance between the barycentres of the cluster of points attained at the
end of different
paths.
- AP is the pose
accuracy, expressing the deviation between a command pose and the mean
of the attained poses
when approaching the
command pose from the same direction (AP is divided into positioning
accuracy and
orientation accuracy).
- RP is the pose repeatability,
expressing the closeness of agreement between the attained poses after
n repeat visits
to the same command
pose in the same direction.
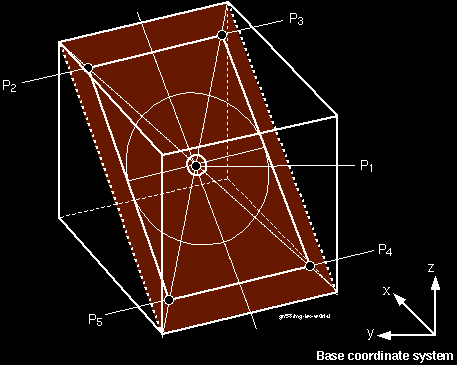
Examples of test paths :
Partners
 |
Fraunhofer-Institut für Produktionsanlagen und
Konstruktionstechnik Division of Control Engineering Dept. of Robot & Systems Control Pascalstraße 8-9, D-10587 Berlin, Germany |
| Krypton Electronic Engineering N.V.
Belgium |
|
 |
Katholieke Universiteit Leuven
Belgium Research & Development Division of Production Enineering, Machine Design and Automation |
| Dassault Aviation S.A.
B.P 289 59472 Seclin France |
|
 |
Robotkonsult AB
Göteborg-Sweden |
 |
Chalmers University of Technology AB (CTH)
Sweden Department of Production Engineering Chalmers Robotics Laboratroy (CRL) |