Quality Function Deployment
Quality Function Deployment, or QFD, is a method used to identify
critical customer attributes and to create a specific link between
customer attributes and design parameters. Matrices are used
to organise information to help marketers and design engineers
answer three primary questions:
- What attributes are critical to our customers?
- What design parameters are important in driving those customer
attributes?
- What should the design parameter targets be for the new design?
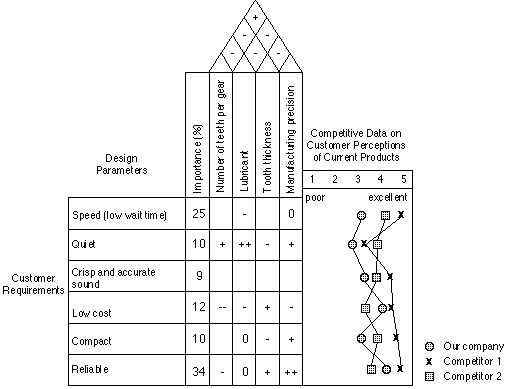
The organising framework for the QFD process is a planning
tool called the "house of quality" (simplified example
above). Working as a team, design engineers and marketers first
establish critical customer attributes for the product. These
attributes become the rows of the central matrix of the house
of quality. The team may group attributes into broader categories
in order to simplify planning and analysis.
In the example above, six attributes have been singled out
for analysis: speed, quiet operation, crisp and accurate sound,
cost, size, and reliability. The team now establishes weightings
that represent the relative importance of each attribute from
the customers' perspective. The complete set of weightings adds
up to 100%.
The second step is to establish the critical design parameters
that drive system performance (in measurable terms and directly
linked to customer attributes). In the example these are: number
of teeth, lubricant, tooth thickness, and manufacturing precision.
The third step is to fill in the body of the central matrix.
Each cell represents a potential link between a design parameter
and a customer attribute. This "relationship matrix"
indicates both the direction and strength of the relationship.
The fourth step focuses on customer perceptions of the company's
existing
product as compared to its competitors. This may give insight
into market problems and opportunities. The fifth and last piece
of analysis is the interaction or relationship between design
parameters. In the cells of the "roof" matrix is indicated
the strength and direction of the interrelationships among design
parameters.
Reference
- Wheelwright. S. C. and Clark. K. B., 1992, Revolutionizing
Product Development, The Free Press, New York.
|