Porter's 5 Forces
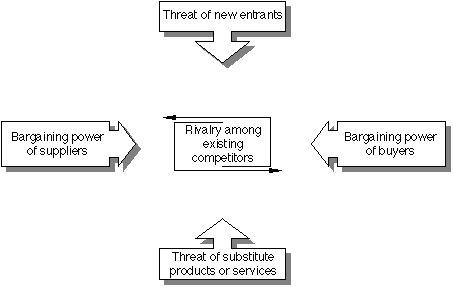
A framework for diagnosing industry structure, built around
five competitive forces that erode long-term industry average
profitability. The industry structure framework can be applied
at the level of the industry, the strategic group (or group of
firms with similar strategies) or even the individual firm. Its
ultimate function is to explain the sustainability of profits
against bargaining and against direct and indirect competition.
Porter's five forces, or factors that shape business strategy
are:
- Threat of entry to the market from other organisations
- Supplier power
- Buyer power
- Availability of substitute products
- Existing competitors
The elements involved with each force are shown in the lists
below
Entry Barriers
- Economies of scale
- Proprietary product differences
- Brand identity
- Switching costs
- capital requirements
- Access to distribution
- Absolute cost advantages
- Proprietary learning curve
- Access to necessary inputs
- Proprietary low-cost product design
- Government policy
- Expected retaliation
Determinants of Supplier Power
- Differentiation of inputs
- Switching costs of suppliers and firms in the industry
- Presence of substitute inputs
- Supplier concentration
- Importance of volume to supplier
- Cost relative to total purchases in the industry
- Impact of inputs on cost or differentiation
- Threat of forward integration relative to threat of backward
integration by firms in the industry
Determinants of Buyer Power
Bargaining Leverage
- Buyer concentration versus firm concentration
- Buyer volume
- Buyer switching costs relative to firm switching costs
- Buyer information
- Ability to backward integrate
- Substitute products
- Pull-through
Price Sensitivity
- Price / total purchases
- Product differences
- Brand identity
- Impact on quality / performance
- Buyers profits
- Decision makers' incentives
Rivalry Determinants
- Industry growth
- Fixed (or storage) costs/value added
- Intermittent over capacity
- Product differences
- Brand identity
- Switching costs
- Concentration and balance
- Informational over complexity
- Diversity of competitors
- Corporate stakes
- Exit barriers
Determinants of Substitution Threats
- Relative price performance of substitutes
- Switching costs
- Buyer propensity to substitute
References
- Porter ME, 1979 Mar/Apr, 'How competitive forces shape strategy',
Harvard Business Review.
- Porter ME, 1980, "Competitive Strategy: Techniques for
Analysing Industries and Competitors". The Free Press.
- Porter ME, "Towards a Dynamic Theory of Strategy",
Strategic Management Journal 1991, vol. 12, 95-117.
|