TQM Tools
Here follows a brief description of the basic set of Total
Quality Management tools. They are:
Classified Index , Alphabetic
Index, Decision Support Homepage
, Strategy Process Chart , Performance Process Chart
Pareto Principle
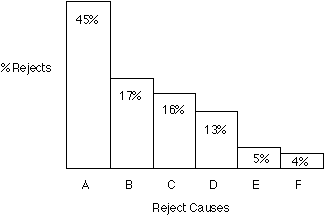
The Pareto principle suggests that most effects come from
relatively few causes. In quantitative terms: 80% of the problems
come from 20% of the causes (machines, raw materials, operators
etc.); 80% of the wealth is owned by 20% of the people etc. Therefore
effort aimed at the right 20% can solve 80% of the problems.
Double (back to back) Pareto charts can be used to compare 'before
and after' situations. General use, to decide where to apply
initial effort for maximum effect.
Reference
- The Tools of Quality; Quality Progress, Nov 1990; J T Burr.
Classified index , Alphabetic
Index, Decision Support Homepage
, Strategy Process Chart , Performance Process Chart
Scatter Plots
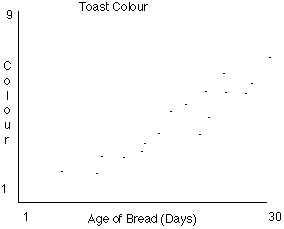
A scatter plot is effectively a line graph with no line -
i.e. the point intersections between the two data sets are plotted
but no attempt is made to physically draw a line. The Y axis
is conventionally used for the characteristic whose behaviour
we would like to predict. Use, to define the area of relationship
between two variables.
Warning: There may appear to be a relationship on the plot
when in reality there is none, or both variables actually relate
independently to a third variable.
Reference
- The Tools of Quality; Quality Progress, Dec 1990; J T Burr.
Classified index , Alphabetic
Index, Decision Support Homepage
, Strategy Process Chart , Performance Process Chart
Top
Control Charts
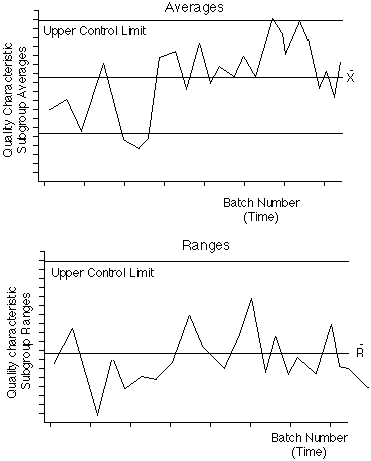
Control charts are a method of Statistical Process Control,
SPC. (Control system for production processes). They enable the
control of distribution of variation rather than attempting to
control each individual variation. Upper and lower control and
tolerance limits are calculated for a process and sampled measures
are regularly plotted about a central line between the two sets
of limits. The plotted line corresponds to the stability/trend
of the process. Action can be taken based on trend rather than
on individual variation. This prevents over-correction/compensation
for random variation, which would lead to many rejects.
Reference
- The Tools of Quality; Quality Progress, Aug 1990; P D Shainin.
Classified index , Alphabetic
Index, Decision Support Homepage
, Strategy Process Chart , Performance Process Chart
Flow Charts
Pictures, symbols or text coupled with lines, arrows on lines
show direction of flow. Enables modelling of processes; problems/opportunities
and decision points etc. Develops a common understanding of a
process by those involved. No particular standardisation of symbology,
so communication to a different audience may require considerable
time and explanation.
Reference
- The Tools of Quality; Quality Progress, June 1990; J T Burr.
Classified index , Alphabetic
Index, Decision Support Homepage
, Strategy Process Chart , Performance Process Chart
Cause and Effect , Fishbone, Ishikawa
Diagram
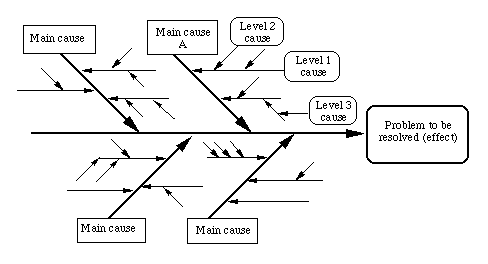
The cause-and-effect diagram is a method for analysing process
dispersion. The diagram's purpose is to relate causes and effects.
Three basic types: Dispersion analysis, Process classification
and cause enumeration. Effect = problem to be resolved, opportunity
to be grasped, result to be achieved. Excellent for capturing
team brainstorming output and for filling in from the 'wide picture'.
Helps organise and relate factors, providing a sequential view.
Deals with time direction but not quantity. Can become very complex.
Can be difficult to identify or demonstrate interrelationships.
References
- Sarazen, JS., The Tools of Quality; Quality Progress, July
1990.
- Production Systems; J L Riggs, Wiley, 1987.
- Production/Operations management; Terry Hill, PHI, 1983.
Classified index , Alphabetic
Index, Decision Support Homepage
, Strategy Process Chart , Performance Process Chart
Top
Histogram or Bar Graph
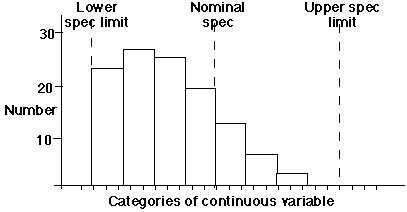
A Histogram is a graphic summary of variation in a set of
data. It enables us to see patterns that are difficult to see
in a simple table of numbers. Can be analysed to draw conclusions
about the data set.
A histogram is a graph in which the continuous variable is
clustered into categories and the value of each cluster is plotted
to give a series of bars as above. The above example reveals
the skewed distribution of a set of product measurements that
remain nevertheless within specified limits. Without using some
form of graphic this kind of problem can be difficult to analyse,
recognise or identify.
Reference
- The Tools of Quality; Quality Progress, Sept 1990; The Juran
Institute.
Classified index , Alphabetic
Index, Decision Support Homepage
, Strategy Process Chart , Performance Process Chart
Check Sheets
A Check Sheet is a data recording form that has been designed
to readily interpret results from the form itself. It needs to
be designed for the specific data it is to gather. Used for the
collection of quantitative or qualitative repetitive data. Adaptable
to different data gathering situations. Minimal interpretation
of results required. Easy and quick to use. No control for various
forms of bias - exclusion, interaction, perception, operational,
non-response, estimation.
Reference
- The Tools of Quality; Quality Progress, Oct. 1990; The Juran
Institute.
Classified index , Alphabetic
Index, Decision Support Homepage
, Strategy Process Chart , Performance Process Chart
Check Lists
A Checklist contains items that are important or relevant
to a specific issue or situation. Checklists are used under operational
conditions to ensure that all important steps or actions have
been taken. Their primary purpose is for guiding operations,
not for collecting data. Generally used to check that all aspects
of a situation have been taken into account before action or
decision making. Simple, effective. |