PATTERN LANGUAGE III/VI
(Example For Internet Navigation)
|
CONNECTIVITY
 Client Client
|
GSM Data
slow Dial Up
fast Dial Up
56K/X2 US Robotics
ISDN
Direc PC Eutelsat II F3
Cablesurf Munich
CyberBlast ENM CBC
EMS Intel
ADSL
Cable TV
DirectTV Adaptec
Echostar Dish Satellite Network
|
9.6 KBit/s
14.4 KBit/s
33.6 Kbit/s
56 KBit/s
128 KBit/s
400 KBit/s
550 KBit/s
2.3 MBit/s
4.5 MBit/s
8 MBit/s
10 MBit/s
30 MBit/s
30 MBit/s
|
 Provider/Intranet Provider/Intranet
|
T1
Ethernet 10BaseT
ATM
Fast Ethernet 100BaseT
FDDI
ATM/OC3
FireWire
ATM/OC12
Fibre Channel
|
1.544 KBit/s
10 MBit/s
25 MBit/s
100 MBit/s
100 MBit/s
155 MBit/s
400 MBit/s
622 MBit/s
800 MBit/s
|
 Internet Internet
|
Giga Ethernet
ATM
ATM
|
1 GBit/s
1.4 GBit/s
2.8 GBit/s
|
 Evaluation Evaluation
|
CD ROM
12 x CD ROM
24 x CD ROM
SCSI
|
150 KBit/s
1.8 MBit/s
3.6 MBit/s
5.0 MBit/s
|
Service Type
Display Time in Seconds
Aprrox bits/sec
14.4KB Multiplier (real world) |
14.4KB
90
8K
1 |
56KB
28
40K
3 |
ISDN
19
100K
5 |
T1
12
1500K
8 |
T3
6
4500K
21 |
LAN
4
10MB
22 |
GSM Global System Mobile Communication
ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network (2 Channel * 64 KBit/s)
FDDI Fibre Distributed Data Interface
EMS European Satellite Multimedia Services
ADSL Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode
 Communication and information channeling Communication and information channeling
Under certain circumstances it is useful to separate the communication and information into different channels, mostly in input and output channels. In the world wide web more than 90 percent of data is downloaded from the content provider, but much less than 10 percent are sent from the participants of the net. This part is much smaller because the user is following only the given navigation and orientation structures, sending mostly only small confirmation or decision signals. Therefore the connectivity of the user output channel could be much lower than the original input channel with its texts, pictures, sounds and other media. An differentiation between these ways or channels (asymmentric information transfer) is useful to increase the overall connectivity.
This technology is used at any kind of ADSL and also satellite broadcasting. They are based on a broad, cheap and fast connection to the single user, company or network and a smaller on in the back direction on the other hand. Because both channels are based on different media, this could save connectivity costs.
(The same technology can be used to share render or computer power in wired environments. Either complex operations can be computed by a strong and fast (and expensive) supercomputer as in the wheather forecast industries, or just in the opposite, many small and simple (and cheap but motivated) personal computer join their forces to solve the given problems as in the cryptography and key hacking programs (RSA crack).


THE TWO CLASS INFORMATION SOCIETY
 The one-way-street information highway The one-way-street information highway
In other words, especially there, where the knowledge or wisdom saved in the internet or other netsystems would be needed for the building of structures, these information are technically suppressed.
This leads up to a further unnecessary intensification of the differences between North and South/ rich and poor (with the results of emigration, persons seeking asylum, refugees, civil war, riots, hunger etc.) - to the development of a two class society of the information systems.
 Connectivity in Africa and Asia Connectivity in Africa and Asia
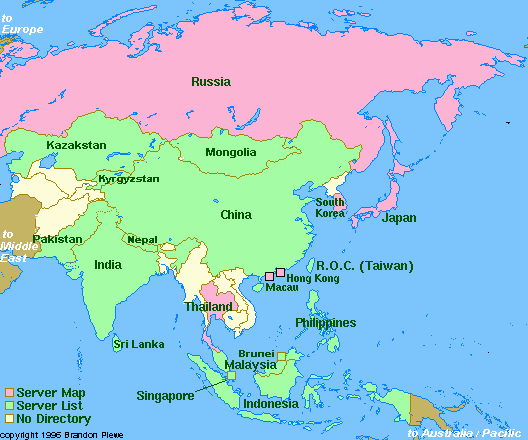
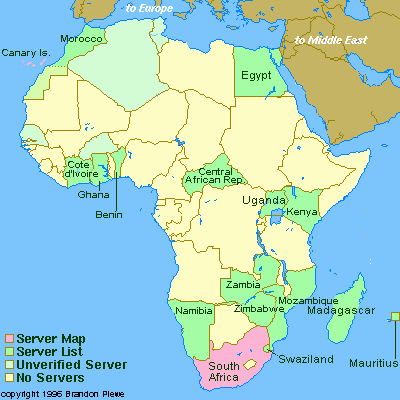
 Connectivity during 8/91 and 6/97 Connectivity during 8/91 and 6/97
The following maps may be obtained also via anonymous ftp from: ftp.cs.wisc.edu/connectivity_table  . The author Larry Landweber gives the unlimited permission to copy or use it if this copyright notice is included. . The author Larry Landweber gives the unlimited permission to copy or use it if this copyright notice is included.
|
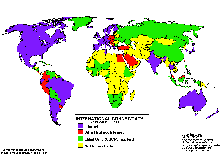
Internet Connectivity 9/91
|
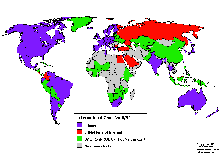
Internet Connectivity 8/92
|
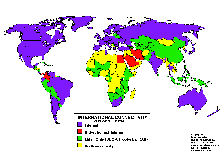
Internet Connectivity 8/93
|
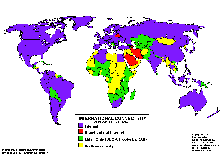
Internet Connectivity 7/94
|
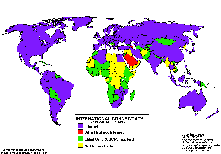
Internet Connectivity 6/95
|
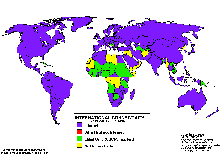
Internet Connectivity 6/96
|

Internet Connectivity 6/97
|
|
|