Less costly than conventional
electronic repeaters, these devices have been effectively replacing electronic
regenerators over recent years because of inherent simplicity and transparency
to bit rate and format. By amplifying light pulses without the need to
perform re-timing and regeneration, optical amplifiers are paving the way
for DWDM, soliton, and advanced optical network schemes of the foreseeable
future. However, complexities include: noise accumulation, non-linear effects,
chromatic dispersion, and polarization phenomena.
Optical Amplifiers are also
being sold at increasing levels. Some sites that contain information
on Optical Amplifiers are:
Fiber
core Fiber Amplifiers
Scitech
Instruments Ltd.
Or to find our more information
on the basic principles of optical amplifiers, Optical amplification in
semiconductor laser diodes, Analysis of transverse modal fields in semiconductor
laser
amplifiers, Analysis and
modeling of semiconductor laser amplifiers: gain and saturation characteristics.
Or Analysis and modeling of semiconductor laser amplifiers, you can order
a report on all the technical specifications from a book by H.
Ghafouri-Shiraz
A picture of one Amplifier
and a model of the signal gain offered by such devices is enclosed below:


Branching Units
Initial branching units were
used to create networks with more than one landing point. These branching
units were either passive or active, while the latter is not commonly used
because of their complexity and expense. Passive branching units are used
to create route diversity and protection, not unlike ADMs in a terrestrial
SDH network. Future branching units will employ wavelength routing and
switching capabilities for true optical networking capabilities.
SONET/SDH
Synchronous Optical Network
(SONET) and (SDH) international standards have pioneered inter operable
global networks with built-in routing, monitoring and control information
in their traffic streams. Both terminal and add-drop multiplexers are transforming
point-to-point into highly reliable complex ring networks . These provide
restoration by switching paths or lines around failed nodes. Majority of
new long-haul systems, including TPC-5CN, TAT-12/13, AC-1, Gemini 1 and
2,
US-China Cable Networks and
others are using ring configurations and SDH transmission for protection
because of inadequate capacity on satellite facilities.
Network Management
Network management has benefited
from deployment of SDH systems, including embedded data communications
channels that carries network management information on each node in the
network and allows for quick identification of faults and other events
in submarine network. In future submarine systems employing WDM, network
management becomes more complex as individual wavelength channels must
be supervised and controlled, as well as optical ADMs. Presently, ITU and
other standards bodies are drafting standards for optical network supervision
and control - most of which include an embedded supervisory channel as
a distinct wavelength channel.
 If you have comments or suggestions, email me at [email protected]
If you have comments or suggestions, email me at [email protected]

This page created with Netscape Navigator Gold
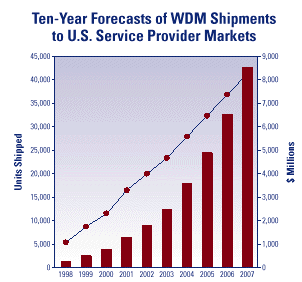
![]()
![]()