Viewing
contents of a directory
A
directory is what you commonly know as folders
in windows. A directory contains file names,
theirs extensions, file size, date last modified
, time last modified, starting location of
the file on the disk and the attributes. To
view the contents of a directory, use the
dir
command.
What
you get is a listing such as this one:
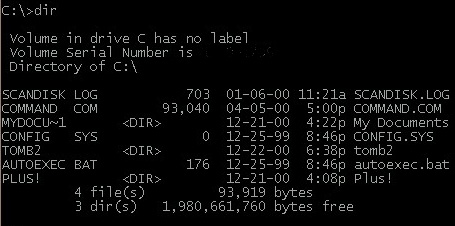
From
the above, all the files with the <DIR>
beside
them are directories.
Changing
directories
To change directories, you use the cd
command, followed by the name of the directory
you want to change to. E.g. from above to
change to the plus! directory your command
will look something like this c:\>CD
plus!. Your prompt after pressing enter
key will look like this c:\plus!>
To go back to the root directory you will
type CD
or CD\
Every
disk must have at least one directory, called
the root directory. A sub-directory
will be more lie a folder within a folder.